Blockchain Basics: What is Blockchain? A Simple Explanation for Beginners”
Table of Contents
- What Is Blockchain Technology in Simple Words?
- Blockchain Meaning
- How Blockchain Works?
- Key Questions About Blockchain
- Main Components of Blockchain
- What is a Smart Contract in Blockchain?
- What is Consensus Mechanism in Blockchain?
- What is Cryptography in Blockchain?
- What’s the Future of Blockchain in 2024?
- Is Blockchain Fully Secure?
- Blockchain Technology and Security Challenges
- Ways to Keep Blockchain Safe
- Blockchain and Transparency
What Is Blockchain Technology in simple words?
Blockchain or Block Chain:
Block and chain are two important parts of Blockchain technology.
Block: A “block” is like a digital box that stored information about transactions.
Chain: When these blocks are connected together in a chain, they are called Blockchain.
Transactions: Transactions means when you exchange something with other person. It may be product, money, knowledge, data or any goods and service. For example, when you buy a toy from a store, you’re making a transaction by giving money in exchange for the toy. It is essential part of every business.
Blockchain Meaning:
Blockchain is a distributed ledger keeps record of all types of transactions. It works across peer to peer network –means person to person.
Ledger: is a digital notebook
Distributed: It means information stored and shared on every page of notebook.
Every transaction is stored, record in Blocks and verified by using decentralization technique. Blockchain is immutable. This means that, no one can change and delete the data without the consensus of network. If one person tries to do the illegal transaction, other interconnected networks of computers achieve notification and in the same way whole chain of network involved to avoid that type of transaction. This is the reason, Blockchain is more secure, transparent and trustworthy data exchange.
How Blockchain works?
Blockchain consists of 3 main components.
- A Block
- A Node
- A minor
You can understand this concept by simple metaphor.
Blockchain is like a long chain of boxes, each connected to the previous one. Each box represents a “block” of information (like transactions).
Here’s How it Works:
New Box Added: When new information is added, a new box (block) is created and attached to the end of the chain.
Locking the Box: The new box is “locked” using a special code (called a “hash”) that connects it to the previous box.
Sealing the Chain: Once the box is locked the entire chain of boxes is “sealed” and can’t be altered.
Many Copies: Many people have a copy of the entire chain of boxes, so everyone agrees on what’s inside.
Verification: If someone tries to alter a box, the chain will break, and everyone will notice.
In the given metaphor,
BOX shows “Block”.
Nodes: are the “many people” who have a copy of the entire chain of boxes.
Miners: are the ones who create the new boxes (blocks) and “lock” them using the special code (hash).
Now everyone asked about the key questions …
Key questions about Blockchain
Who invented Blockchain?
Blockchain was invented by group of anonymous people called Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. In October, first Blockchain white paper was published about bitcoin named as “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”. Satoshi Nakamoto is the name used by the person or people who made Bitcoin. Nobody knows for sure who Satoshi Nakamoto really is. Some thought Dorian Nakamoto was Satoshi, but he said it wasn’t him. Craig Wright says he’s Satoshi, but many don’t believe him. Another idea is that Nick Szabo, who made Bit Gold, might be Satoshi.
Where Blockchain data is stored?
The Blockchain data is stored and encrypted in blocks. Block is the basic unit of Blockchain. It is like a square box which contain all information of transaction, where you buy, where to sell, and where you transfer money.
What is decentralization in Blockchain?
Decentralization in Blockchain means:
- No single person or organization controls the data or network.
- Data is stored on many computers (nodes) around the world.
- Everyone has a copy of the data, so it can’t be altered or deleted.
- Decisions are made by a group, not just one person.
- This makes Blockchain secure, transparent, and fair!
What is ledger in Blockchain Technology with example?
A ledger is a system which record transactions. It is like a bookkeeper tracking income and expenses. But instead of being stored in one place, it’s shared across many computers, making it secure, transparent and trustworthy.
For Example: Bitcoin ledger is a decentralized, digital record book that stores all Bitcoin transactions. It’s made up of multiple blocks, each containing a collection of transactions.
What are the main components of blockchain?
Here are the main components of Blockchain:
- Distributed Ledger
- Blocks
- Transactions
- Nodes
- Consensus Mechanism
- Cryptography
- Smart Contracts
- Network Protocol
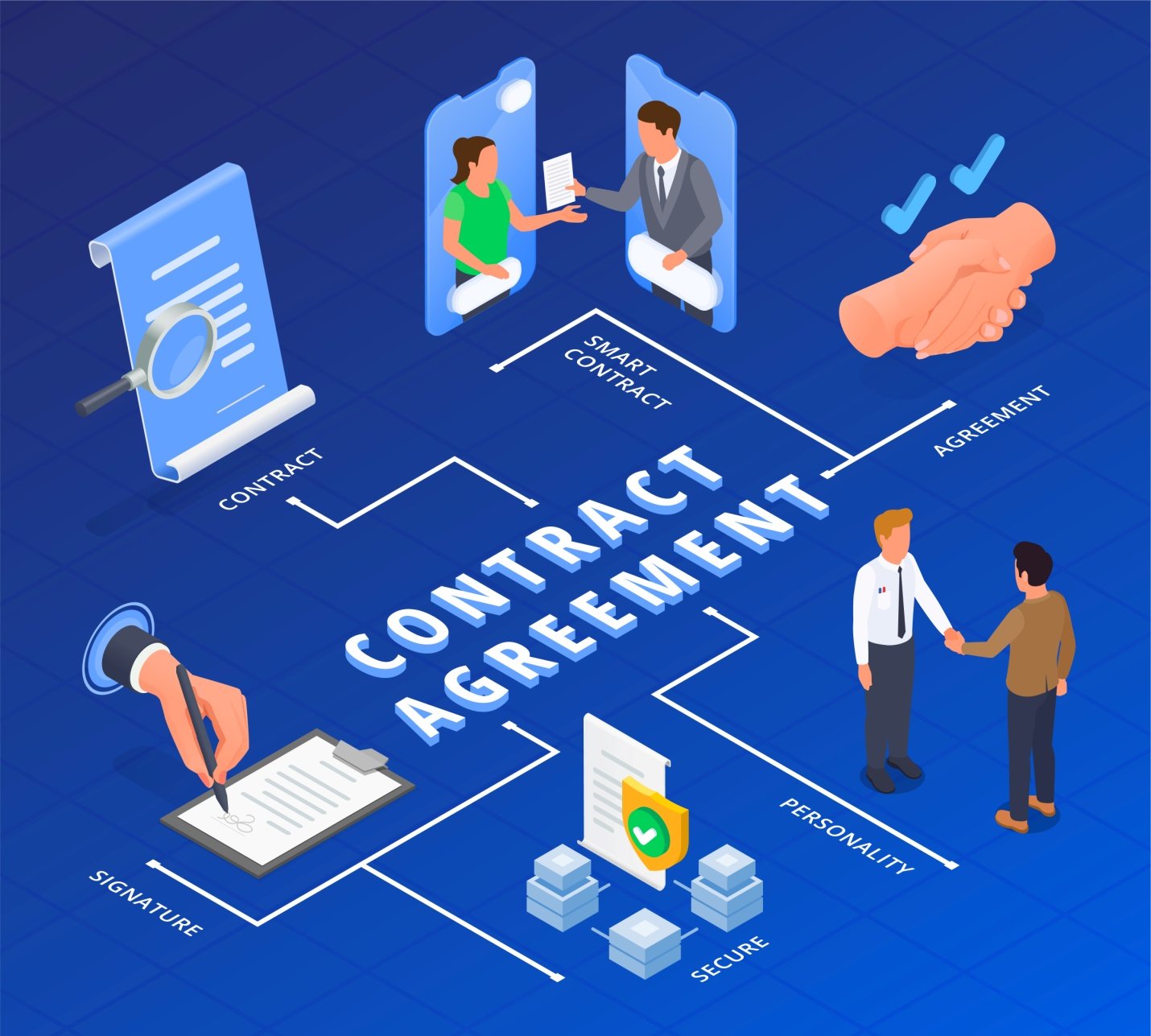
What is smart contract in Blockchain?
What is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is like a digital agreement between two people. It’s a set of rules that are automatically followed when something happens.
Think of it like a Vending Machine:
- You put in money (follow the rules)
- You select what you want (agree to the terms)
- The machine gives you what you want (automatic execution)
How Smart Contracts Work:
- Write the Rules: Someone writes the rules of the agreement (the smart contract).
- Put it on the Blockchain: The rules are stored on a special kind of computer called a blockchain.
- Follow the Rules: When something happens, the Blockchain checks the rules and follows them automatically.
What Smart Contracts Can Do:
- Automate Agreements: Smart contracts can automatically execute agreements between people, like transferring money or sending goods.
- Secure and Transparent: Smart contracts are stored on a blockchain, making them secure and transparent.
- No Third party: Smart contracts don’t need a third party to enforce the rules making them faster and cheaper.
In Simple Terms:
Smart contracts are like digital rules that are followed automatically, making agreements between people faster, cheaper, and more secure.

What is consensus mechanism in Blockchain?
Imagine a group of people making a decision together. They need to agree on something, like what to eat for dinner. But, they are all different and have different opinions. Consensus is when they all agree on one thing, even if it’s not their first choice.
Consensus in Blockchain
In blockchain, computers (called nodes) need to agree on what transactions are valid. This is called consensus. It’s like the group of people agreeing on dinner, but with computers and transactions!
Why is Consensus Important?
Consensus helps keep the blockchain safe and honest. It makes sure that:
- Transactions are valid
- Nodes agree on the order of transactions
- The blockchain is updated correctly
Common Consensus Mechanisms
There are a few ways to reach consensus in blockchain. Some popular ones include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Nodes solve a hard math problem to agree on transactions.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Nodes put up some of their own money (or “stake”) to agree on transactions.
These mechanisms help nodes agree and keep the blockchain secure.
What is cryptography in Blockchain?
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is like a secret code that keeps information safe and private. It’s like sending a secret message that only the intended person can read.
How Does it Work in Blockchain?
In blockchain, cryptography is used to:
- Lock and Unlock: Keep transactions (like money transfers) safe and secure, like a digital lock.
- Verify Identity: Make sure the person sending or receiving is who they claim to be.
- Keep Data Private: Protect the information being sent, so only the intended person can see it.
Two Main Types of Cryptography:
- Public Key Cryptography: Like a pair of keys. One key (public) is used to lock, and the other key (private) is used to unlock.
- Hash Functions: Like a digital fingerprint. It takes a piece of data and creates a unique code that can’t be changed.
In Simple Terms:
Cryptography in blockchain is like using secret codes to keep information safe and private. It helps secure transactions, verify identities, and protect data, making blockchain a trustworthy and secure way to transfer value and information
What’s the future of Blockchain in 2024?
The future of Blockchain technology in 2024 and beyond looks promising. 2023 was a tough year for Blockchain (COINDESK). It faced legal problems and big company changes. The Blockchain and cryptocurrency world has had its ups and downs, but NORQUE is changing the game. “NORQUE is a new project that combines AI, machine learning, and Blockchain to offer risk management services and more.
Is Blockchain fully secure?
Blockchain is secured with cryptographic principles. But it’s not completely immune to threats or vulnerabilities. Here’s a balanced view:
Security strengths:
- Decentralized network: Many computers work together, making it hard for one person to control.
- Cryptographic algorithms: Secret codes keep data safe.
- Immutable ledger: Transactions are recorded permanently and can’t be erased.
- Consensus mechanisms: All Nodes agree on one decision making of blockchain, it preventing manipulation.
Security Risks:
- Smart contract bugs: Errors in smart contract code can lead to security issues.
- Node compromise: If a significant number of nodes are hacked, the network can be in trouble.
- 51% Attack: A group controlling over 50% of the network’s mining or validation power can launch an attack.
- Phishing and social engineering: Users can still be tricked into revealing private keys or sensitive information.
Blockchain and security
Security Challenges
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize many industries, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. However, like any new technology, it faces security challenges that could undermine its potential and put users at risk.
Main Security Challenges
One of the main security challenges facing blockchain is:
- 51% Attack: These is when a group of people gains control of most of the computing power on a blockchain network, allowing them to manipulate transactions, steals coins, or prevent others from verifying transactions. This is more likely to happen on smaller networks. In January 2019, the Ethereum Classic network was attacked by a group of actors who gained control of most of the network’s computing power. This allowed them to steal around $1.1 million worth of Ethereum Classic coins. To prevent this, blockchain networks can use different algorithms like proof-of-stake or proof-of-authority, or implement security measures like checkpoints or alert systems.
Other security challenges include:
- Double-spending attacks
- Smart contract vulnerabilities
- Phishing attacks
- Malware and ransomware attacks
- Insider threats
Blockchain and cryptography
Cryptography is like a lock that keeps blockchain safe. Cryptography is the backbone of blockchain security, ensuring that data and transactions are safe and secure. But even cryptography can be hacked or broken into, especially with new technologies like quantum computing and artificial intelligence. In 2020, a hacker broke into 49 Bitcoin wallets and stole a lot of money ($470,000). This happened because the cryptography was not strong enough. This breach highlights the need for stronger and more resilient cryptographic algorithms and protocols to protect blockchain networks and applications.
To prevent this from happening again, blockchain networks and applications need to:
- Use stronger cryptography methods
- Update their systems regularly
- Stay ahead of new threats and technologies
Ways to Keep Blockchain Safe
Here are some ways to keep blockchain safe:
- Use up-to-date software and hardware. This helps fix bugs and makes the network stronger.
- Use encryption and authentication. This keeps data secret and makes sure only authorized people can access it.
- Use special rules and protocols. These help the network agree on what’s true and what’s not.
- Use smart contracts and oracles. These help automate transactions and make sure they’re correct.
- Keep an eye on the network and transactions. This helps find and fix problems before they become big issues.
Blockchain and Transparency
What It Means:
Blockchain transparency means that all transactions and data on the blockchain are open and visible to everyone. This means that:
- All transactions are recorded publicly
- Anyone can see the entire history of transactions
- All data is stored in a public ledger
- Anyone can access and view the blockchain
Why Transparency is Important
Transparency is important because it:
- Helps build trust in the blockchain
- Prevents fraudulent activities
- Allows for accountability
- Enables anyone to verify transactions
- Makes the blockchain secure and reliable
In short, blockchain transparency means that everything on the blockchain is open and visible, making it a secure and trustworthy way to store and transfer data.


One thought on “Blockchain Basics: What is Blockchain? A Simple Explanation for Beginners””